Clinical trials
 A clinical trial is a research study to evaluate new potential treatments in humans. During a clinical trial, information is collected to determine if a study drug is safe and effective, as well as to evaluate the risks and benefits of the study drug.
A clinical trial is a research study to evaluate new potential treatments in humans. During a clinical trial, information is collected to determine if a study drug is safe and effective, as well as to evaluate the risks and benefits of the study drug.
Prior to clinical trials, pre-clinical testing of the active substance is carried out in the laboratory to evaluate the safety of a drug before it is given to humans.
The drug is developed as a pharmaceutical formulation with the aim of delivering the active substance to its target properly. All the components of the drug must be fully characterized and of high purity, in line with pharmaceutical regulation requirements.
A marketing authorization application (MAA) is then submitted to a regulatory agency (e.g. FDA or EMA) whose mission is to evaluate the risk-benefit profile of the drug in terms of efficacy and safety.
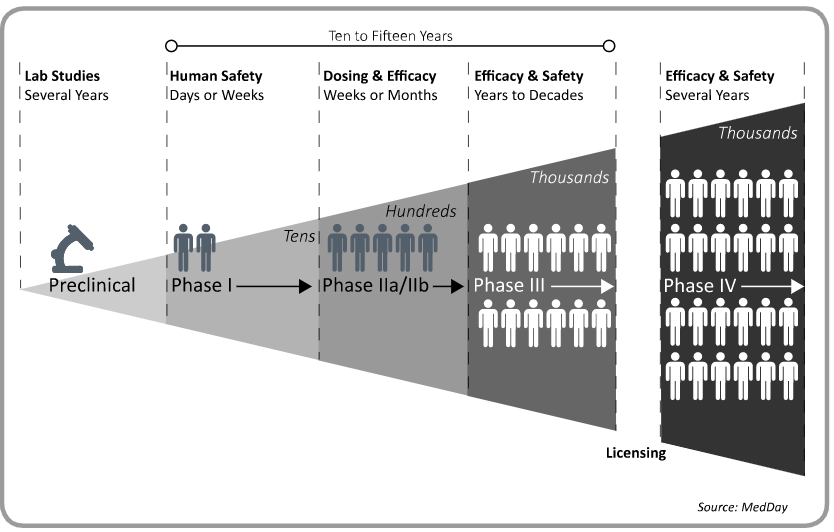
Phases of a clinical trial
Phase I: This type of study includes a small number of healthy volunteers and is used to determine if a drug is safe. These studies allow the definition of the maximum tolerated dose.
Phase IIa: Similar to a Phase I study, a Phase IIa study also measures safety; however, only patients who have the disease which the drug is targeting are included. These studies attempt to determine whether or not the drug modulates the course of the disease.
Phase IIb: A larger number of patients who have the targeted disease are included in Phase IIb studies, which measure how well the drug works (efficacy) in addition to safety. These studies will also determine the best dose to test in future larger studies.
Phase III: A Phase III study is used to confirm efficacy seen in earlier stage trials and monitor adverse reactions.
If positive results are achieved, a biotech or pharma company may apply for approval to market the drug with the appropriate drug regulation organization, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the US or the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe. The application contains all data gathered about the safety and efficacy of the study drug from the above studies. The regulatory agency reviews the data and, if approved, the new treatment can be marketed and distributed to the public.
Phase IV: Post marketing studies are performed after regulatory agency approval to collect additional information including the drug’s risks, benefits, and optimal use in a broader patient population.
For more information about clinical trials in general, please visit https://clinicaltrials.gov.
Our pipeline
MedDay has stopped the development of its lead candidate in progressive forms of Multiple Sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases.
