The SPECMET platform
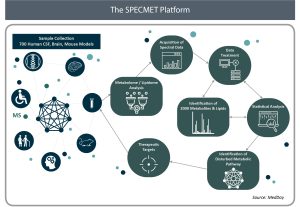 The SPECMET research platform’s main mission is to identify new and promising therapeutic targets for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, where there is a high unmet medical need. The SPECMET platform is focused on three main Research and Development (R&D) areas to discover new therapeutic targets:
The SPECMET research platform’s main mission is to identify new and promising therapeutic targets for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, where there is a high unmet medical need. The SPECMET platform is focused on three main Research and Development (R&D) areas to discover new therapeutic targets:
1. Identify biomarkers and specific metabolic signatures
The first area of research consists in the identification of biomarkers and specific metabolic signatures through untargeted liquid chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry (LC/HRMS) based-metabolomic and lipidomic analyses of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It works by screening CSF from patients with various central nervous system disorders to identify disruptions of metabolic pathways that ultimately cause cell death. Compounds that are known to affect these metabolic pathways are then identified and further developed. Based on the metabolic signatures identified by SPECMET in some neurological conditions, drug candidates can progress into preclinical studies and, if successful, have the potential to move rapidly into clinical development. Unlike other screening techniques that examine the blood of patients, the SPECMET platform allows researchers to screen CSF, which is thought to be more useful given its proximity to neuronal and glial cells. The SPECMET platform seeks to achieve objectives previously considered unreachable.
2. Elucidate mechanism of action
The second R&D area aims to elucidate the mechanism of action of therapeutic drug candidates in animal models and/or in patients in the course of clinical trials. This is achieved in both targeted and untargeted LC/HRMS-based metabolomic and lipidomic analyses in treated versus untreated biological samples.
3. Develop analytic methods to generate insights
Finally, to ensure the accuracy of findings and to increase the coverage of metabolites, the team focuses its efforts on analytical development, data analysis and the development of tools for biological interpretations.
In order to significantly strengthen the SPECMET research platform, MedDay acquired the health division of Profilomic SA, an innovative spin-off company from the Comité d’Energie Atomique (CEA), in 2017. This acquisition allowed MedDay to significantly extend its database and laboratory equipment alongside a team of highly skilled and pioneering scientists with world-class expertise in the fields of metabolomics and lipidomics.
Through strong collaborations with multiple academic institutions, SPECMET has created a biobank of 700 cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples from all major neurodegenerative diseases as well as rare inborn errors of metabolism. LC/HRMS-based metabolomic and lipidomic studies have been set up to examine approximately 2000 small compounds per CSF sample, including various classes of lipids.
Our private – public partnerships

The SPECMET platform, developed in partnership with several large French institutes, is state-of-the-art technology that can be used for the metabolomic analyses of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF):
- A large collection of CSF samples from patients and of tissues from animal models is part of a collaboration with Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris (APHP) and other international Health and Scientific Institutes
- The strong expertise and know-how of the SPECMET team regarding metabolomic and lipidomic analyses by mass spectrometry is strengthened continuously and collectively with the Laboratoire d’Etude du Métabolisme du Médicament (LEMM), which is one of the leaders of metabolomics in France
- SPECMET is working together with a Mexican pharmacy, located at Mexico City, to refine dedicated metabolomic network tools that can integrate and map large analytical data sets
- Through its strategic partnerships with CEA and INRA, SPECMET participates in the development of metabolomic and lipidomic methods for MetaboHub (French Infrastructure in metabolomics and fluxomics)

Publications
CEREBROSPRINAL FLUID METABOLOMICS HIGHLIGHTS DYSREGULATION OF ENERGY METABOLISM IN OVERT HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
Weiss N, et al. J Hepatol. 2016 Dec;65(6):1120-1130. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.046. Epub 2016 Aug 9 [abstract]
METEXPLOREVIZ: WEB COMPONENT FOR INTERACTIVE METABOLIC NETWORK VIZUALIZATION
Chazalviel M, et al. Bioinformatics. 2017 Sep 15. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx588 [abstract]
METABORANK: NETWORK BASED RECOMMENDATION SYSTEM TO INTERPRET AND ENRICH METABOLOMICS RESULTS
Frainay C, et al. Bioinformatics. 2018 Jul 6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty577 [abstract]
TARGETED VERSUS UNTARGETED OMICS – THE CAFSA STORY
Del Mar Amador M, et al. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018 May; 41(3):447-456. doi: 10.1007/s10545-017-0134-3. Epub 2018 Feb 8 [abstract]
